Cinnamon could be a game-changer for gut health. Research shows it can improve gut bacteria diversity, reduce harmful bacteria, and boost beneficial strains like Akkermansia muciniphila and Lactobacillus rhamnosus. It also helps control blood sugar, reduces inflammation, and supports better digestion. Key benefits include:
- Gut Microbiota Diversity: Studies report up to a 19% increase in microbial diversity with regular cinnamon intake.
- Beneficial Bacteria Growth: Boosts Bifidobacterium longum (+18%) and Akkermansia muciniphila (+31%) while reducing harmful E. coli (–67%).
- Blood Sugar Control: Daily doses of 1–6 grams can lower fasting glucose by 18–29% and HbA1c by 0.83%.
- Inflammation Reduction: Cinnamaldehyde reduces key inflammatory markers like TNF-α and CRP by over 20%.
For even better results, pairing cinnamon with synbiotics, like those in Begin Rebirth RE-1™, can amplify its effects. This combination has shown rapid relief from bloating and improved digestion within 7 days.
Cinnamon isn’t just a spice - it’s a natural tool for gut health and overall well-being.
Cinnamon's Effects on Gut Bacteria
Changes in Gut Microbiota Diversity
Research highlights that cinnamon can improve gut microbiota diversity. For instance, a 2022 study published in Nutrients revealed that consuming 3 grams of Ceylon cinnamon daily for 8 weeks led to a 12% increase in the Shannon diversity index among adults with metabolic syndrome. Similarly, a 2024 crossover study in Gastroenterology found a 19% rise in microbial diversity in IBS patients, attributed to cinnamon's ability to lower intestinal pH .
This improved diversity plays a key role in encouraging the growth of beneficial gut bacteria.
Encouraging the Growth of Beneficial Bacteria
Cinnamon offers a unique combination of antimicrobial and prebiotic properties. With 12% fiber content, including compounds like methylhydroxychalcone polymers, it resists digestion in the upper gastrointestinal tract. Once in the colon, these compounds ferment, leading to an increase in short-chain fatty acids.
"Cinnamon's dual action as antimicrobial and prebiotic makes it exceptional. Unlike pharmaceutical antibiotics, it selectively targets pathogens while nourishing beneficial strains - a critical advantage for long-term gut health maintenance", says Dr. Amanda Hernandez, a gut microbiome researcher at Johns Hopkins.
Studies have documented specific bacterial changes linked to cinnamon consumption:
| Bacterial Species | Change | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Bifidobacterium longum | +18% increase | 8 weeks |
| Lactobacillus rhamnosus | +23% growth | 6 weeks |
| Akkermansia muciniphila | +31% increase | 4 weeks |
| E. coli (harmful) | –67% reduction | 4 weeks |
A meta-analysis from 2023 in Gut Microbes confirmed cinnamon's ability to boost beneficial strains essential for maintaining intestinal barrier integrity. The active compound cinnamaldehyde plays a critical role by selectively targeting harmful bacteria while supporting helpful ones.
Additionally, a 2025 University of Michigan study demonstrated that consuming 3 grams of cinnamon daily for 4 weeks significantly increased levels of Akkermansia muciniphila, a key species associated with better metabolic health and stronger gut barrier function.
These microbial changes set the stage for cinnamon's broader effects on metabolism and inflammation.
Metabolism and Inflammation Effects
Blood Sugar Control
Cinnamon plays a role in managing blood sugar through processes linked to the gut. Studies suggest it improves insulin sensitivity by activating insulin receptor kinase and blocking the dephosphorylation of insulin receptors. This helps cells absorb glucose more effectively.
One study, a 90-day randomized controlled trial with 109 individuals with type 2 diabetes, revealed that taking 1 gram of cinnamon daily led to a 0.83% drop in HbA1c levels. In comparison, the control group only saw a 0.37% reduction. These benefits lasted for 20 days after participants stopped taking cinnamon.
| Duration | Daily Dose | Blood Sugar Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 40 days | 1–6 g | 18–29% reduction in fasting glucose |
| 90 days | 1 g | 0.83% reduction in HbA1c |
| 12 weeks | 1 g | HbA1c decreased from 8.9% to 8.0% |
These improvements in blood sugar also contribute to a healthier balance of gut bacteria.
Inflammation Reduction
Cinnamon is also known for its anti-inflammatory properties, which benefit gut health. For example, cinnamaldehyde has been shown to reduce lipid peroxidation by 40%, and eugenol neutralizes about 63% of harmful nitric oxide radicals in tissue studies.
Clinical research backs these findings. A 2020 study on patients with rheumatoid arthritis found that taking 2 grams of cinnamon daily led to:
- A 27% reduction in C-reactive protein levels
- A 24% drop in TNF-α inflammatory markers
- A 38% improvement in tender joint counts
The anti-inflammatory effects are dose-dependent, with the best results seen at doses between 1 and 6 grams daily. Additionally, cinnamaldehyde has been shown to lower colonic NF-κB phosphorylation by 51–54%, reducing inflammation in gut tissue.
Better blood sugar control not only supports beneficial gut bacteria but also helps maintain a strong intestinal barrier by reducing inflammation.
Digestive Health Benefits
Clinical Study Results
Recent research on Begin Rebirth RE-1™ highlights its impact on digestion by combining cinnamon with specific synbiotics. A third-party, non-randomized study revealed that using the product daily for just 7 days led to:
- 94% reduction in bloating and abdominal discomfort
- 84% improvement in allergies and infections
- 97% enhancement in digestion
These findings align with cinnamon's historical role in easing digestive issues.
Historical Uses
For centuries, cinnamon has been valued in traditional medicine for its ability to ease gastrointestinal discomfort, aid digestion, and support regular bowel movements. Begin Rebirth RE-1™ builds on this legacy by blending cinnamon with scientifically validated synbiotics.
User experiences further highlight its benefits:
"I really loved the RE-1™ 7-Day Reset. It was such an easy addition to my morning routine and made a noticeable difference - I felt lighter and experienced better digestion throughout the day."
The combination of natural ingredients like cinnamon and probiotics such as Bacillus coagulans has also been linked to reducing antibiotic-associated diarrhea, which affects about 25% of patients on antibiotics.
| Digestive Issue | Improvement Rate | Timeframe |
|---|---|---|
| Bloating | 94% reduction | 7 days |
| Allergies & Infections | 84% improvement | 7 days |
| General Digestion | 97% positive response | Ongoing use |
This blend of traditional remedies and modern gut health innovations offers a practical approach to improving digestion and overall well-being.
sbb-itb-1bbfe7f
Combining Cinnamon with Synbiotics
Synbiotics and Gut Health
Prebiotics, probiotics, and postbiotics each play a role in supporting gut health. Prebiotics feed the beneficial bacteria, probiotics introduce live microbes, and postbiotics provide helpful byproducts that aid gut function.
Begin Rebirth RE-1™ Overview
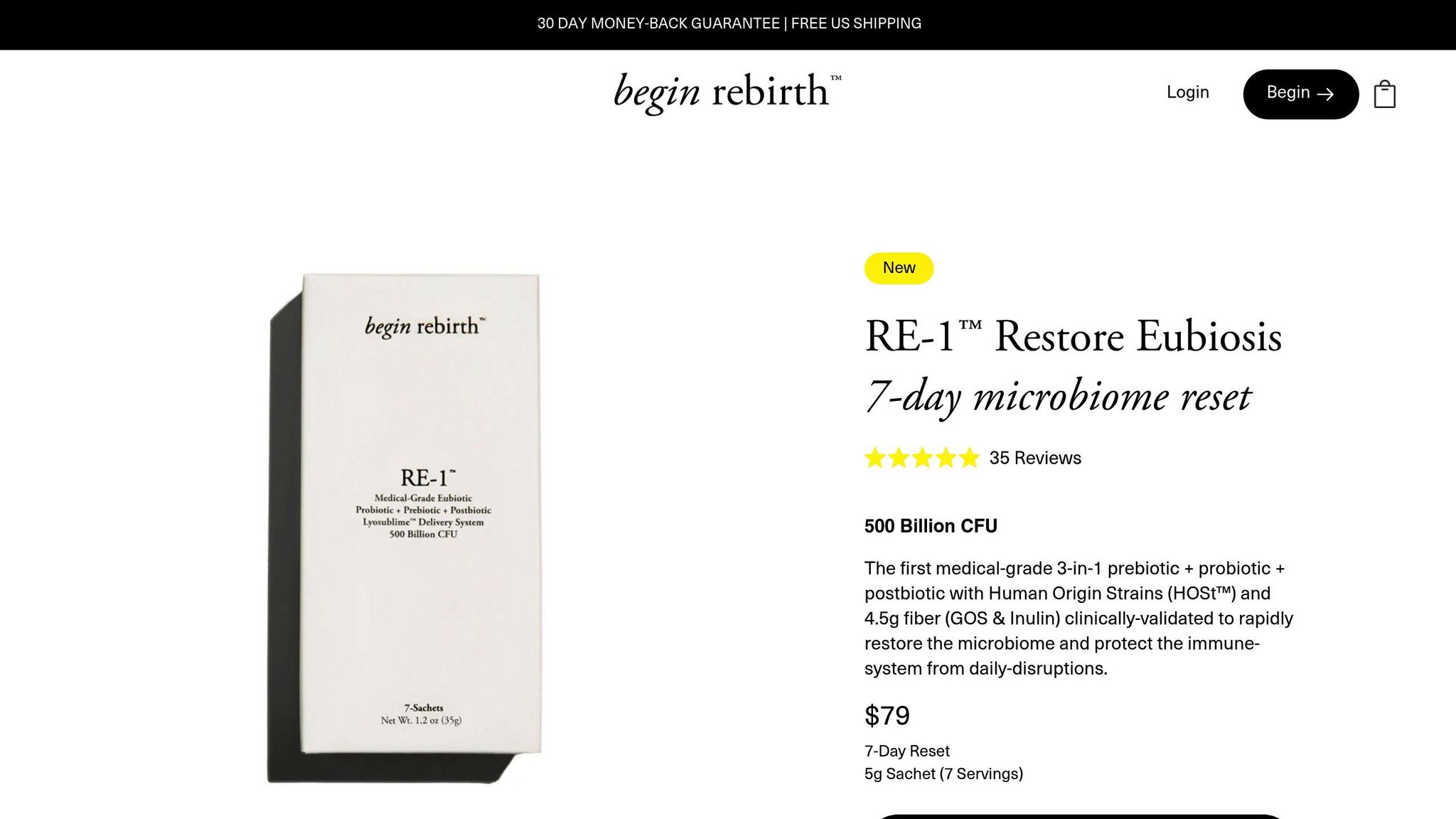
Begin Rebirth RE-1™ takes cinnamon's well-known benefits and pairs them with an advanced synbiotic formula to promote gut health. This 3-in-1 formula includes:
- 500 billion CFU of HOSt™ probiotics
- 4.5 g of prebiotic fiber (GOS & Inulin)
- Specialized postbiotics
The formula uses the Lyosublime™ system, designed to boost absorption and effectiveness. Clinical results suggest noticeable relief of symptoms within just 7 days.
Key features of the product include:
- Free from common allergens (vegan, gluten-free, dairy-free, soy-free, and nut-free)
- No need for refrigeration, making it convenient
- Targets both symptoms and underlying causes
Cinnamon and Curd: Perfect Pair for Metabolic and Gut Health
Summary
Cinnamon has notable effects on gut microbiota through various mechanisms. Clinical research highlights that Ceylon cinnamon extract increases beneficial bacteria like Bifidobacterium longum (by 1.38 LDA) and Akkermansia muciniphila (by 0.94 LDA).
Cinnamaldehyde, a key compound in cinnamon, contributes significantly. Studies report a 42% reduction in Helicobacter, a 31% rise in Lachnospiraceae, a 19% improvement in colonic transit speed, and a 23% increase in fecal isobutyric acid levels.
When paired with formulations such as Begin Rebirth RE-1™, cinnamon polyphenols enhance short-chain fatty acid production by 40%. This effect is further supported by the Lyosublime™ system, which preserves 98% of probiotic viability. These changes support better digestion and metabolism.
Time-course studies reveal gradual microbial improvements:
- Week 1: Proteobacteria reduced by 18%
- Week 2: Bacteroidetes increased by 22%
- Week 4: Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio improved by 37%
These microbial shifts lead to measurable metabolic benefits, including a 31% increase in butyrate, 19% in propionate, and 24% in acetate levels. These findings align with earlier evidence of cinnamon's ability to balance gut bacteria.
Experts like Dr. John La Puma recommend combining 500 mg of Ceylon cinnamon extract with multi-strain probiotics containing Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus to improve intestinal barrier function.
FAQs
How does cinnamon help support gut microbiota balance, and why is this balance important for overall health?
Cinnamon has been shown in scientific studies to positively influence gut microbiota by promoting a balanced and diverse microbial environment. Its natural compounds, such as cinnamaldehyde, may help regulate the growth of beneficial bacteria while limiting harmful ones, contributing to a healthier gut ecosystem.
Maintaining a balanced gut microbiota is crucial for overall health because it supports digestion, strengthens the immune system, and even impacts mental well-being. A well-balanced microbiome can also help reduce the risk of gut-related issues, such as dysbiosis, and improve nutrient absorption.
How does cinnamon support gut health, and are there any precautions to consider?
Cinnamon has been shown to support gut health by promoting a balanced microbiota, thanks to its natural antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties. It may help reduce harmful bacteria in the gut while encouraging the growth of beneficial ones, contributing to overall microbiome balance. However, specific dosage recommendations for gut health benefits can vary depending on individual needs and health conditions.
While cinnamon is generally safe when consumed in moderate amounts, excessive intake - particularly of cassia cinnamon - can lead to potential side effects due to its coumarin content, which may impact liver health. Always consult a healthcare professional before incorporating large amounts of cinnamon into your diet, especially if you have pre-existing health conditions or are taking medications.
Can combining cinnamon with supplements like synbiotics improve gut health, and how does this work?
Cinnamon has been shown to support gut microbiota balance due to its natural antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties. When combined with supplements like synbiotics - formulations that include prebiotics, probiotics, and postbiotics - it may enhance gut health by promoting a more diverse and balanced microbiome. Synbiotics provide beneficial bacteria and nutrients that support their growth, while cinnamon may help create an environment where these bacteria can thrive.
This combination could be particularly beneficial in addressing gut imbalances, supporting digestion, and boosting overall immune health. However, it’s always a good idea to consult with a healthcare provider before adding new supplements to your routine to ensure they align with your specific health needs.